Operational Support Systems (OSS) and Business Support Systems (BSS) are the tools that help network operators manage their most important assets including:
There are many, many building blocks that make up a network operator’s entire support system estate.
Like the TM Forum TAM (The Application Map) before it, the TM Forum ODA Component Library attempts to bring a level of standardisation of all those building blocks, making the entire estate more modular.
Whilst this article will provide a FAQ about the ODA Component Library, we often find the TAM is still widely used. Because the ODA CL and TAM can be overkill for some customers, we often use a Simplified TAM model (the 15 blue boxes) are each a summarised bundle of multiple TAM categories (yellow and grey boxes), as shown below.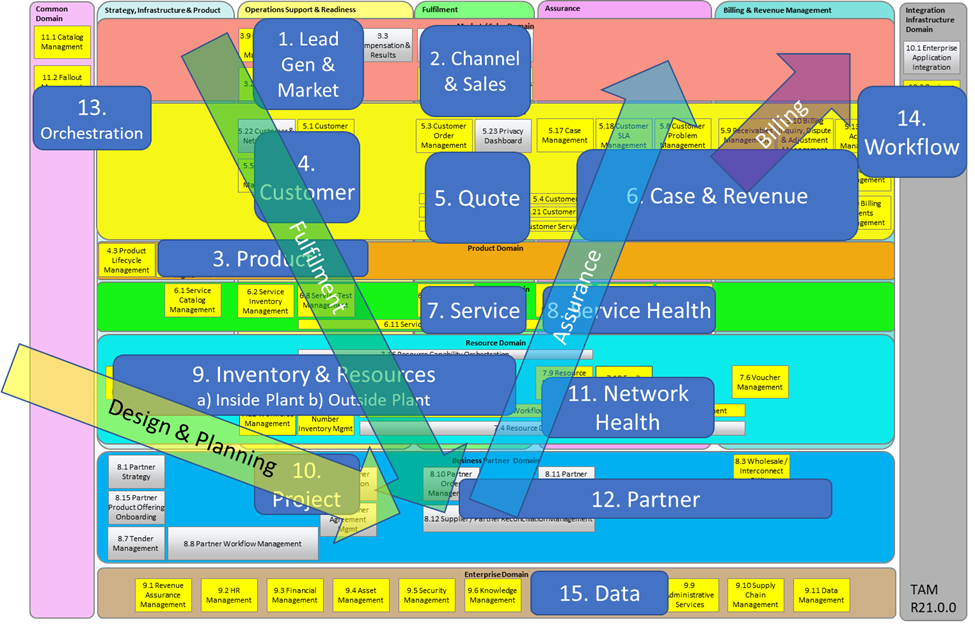
With classification of the 15 Simplified TAM building blocks detailed as follows:

The Open Digital Architecture (ODA) Component Library is a catalogue of modular building blocks defined by TM Forum, the global industry body for telecommunications. Each component represents a clear business or technical capability, such as Product Catalogue Management or Fault Management.
The library provides a common blueprint for moving away from legacy operational and business support systems (OSS and BSS) towards a modern, cloud-native, and interoperable environment. It allows operators and vendors to work from the same playbook, reducing the time and cost of integration.
The Component Library is the evolution of TM Forum’s TAM (Telecom Application Map), which was first published in the early 2000s.
While TAM was widely used, it described “what” needed to exist but not “how” to make it interoperable. ODA takes that next step:
It makes components modular and loosely coupled
It specifies which Open APIs can connect them
It supports cloud-native deployment models, aligning telecom IT with modern enterprise software practices
Telecom operators face huge pressure:
Revenue growth is slowing (global telecom revenue growth is projected at just 1–2% CAGR through 2030 according to GSMA)
Costs are rising due to 5G, edge, and fiber rollouts
Legacy OSS/BSS stacks are too rigid, expensive, and slow to adapt
The ODA Component Library solves these problems by enabling:
Vendor Interoperability: CSPs can mix-and-match vendor solutions instead of being locked into monoliths
Faster Innovation: standardised APIs mean new services can be launched in weeks, not years
Cloud-native agility: supports microservices, DevOps and automated scaling.
Lower Integration Costs: TM Forum estimates CSPs can cut IT integration costs by up to 40% by adopting ODA
The ODA Component Library is designed for use by:
CSP Architects & CIOs: to design digital solution stacks and transformation roadmaps
OSS/BSS Vendors: to ensure their products align with TM Forum standards, making integration with other solutions easier and faster
System Integrators: to reduce complexity in multi-vendor deployments
Regulators & Partners: to guide digital ecosystems and complex interoperability
The ODA CL, TAM and Simplified TAM are all designed to solve the following problems in practice:
Fragmented IT stacks: replaces (or integrates with) dozens of siloed systems with modular, reusable components
Vendor lock-in: CSPs gain the ability to more easily swap vendors without rewriting entire architectures
Slow time-to-market: new digital services and enterprise bundles can be launched faster using pre-defined APIs
Operational complexity: provides a “map” of all functions a digital service provider needs, preventing duplication and/or blind spots in their functionality stack
Now, let’s get into a deeper-dive, answering questions on every one of the ODA components.
.
Q: What is API Management used for?
A: API Management provides a centralised way to expose, secure, monitor and govern APIs across all ODA components. It ensures that services can be accessed consistently, both internally and externally, without bespoke integration effort
Q: Is API Management considered an OSS or BSS function?
A: API Management is a cross-cutting capability that supports both OSS and BSS. It is not confined to one domain because APIs are used to connect systems across the entire architecture, from network resources to customer billing
Q: Why is API Management critical in ODA?
A: Without API Management, components would need direct and often bespoke integrations, leading to higher cost and slower time-to-market. Centralised API Management enforces standards such as TM Forum Open APIs, which are already adopted by most global service providers
.
Q: What is Enterprise Integration used for?
A: Enterprise Integration enables different ODA components, and legacy systems where necessary, to communicate effectively. It provides messaging, orchestration and transformation capabilities so that systems exchange data in a standardised and reliable way
Q: Is Enterprise Integration an OSS or BSS function?
A: Like API Management, it cuts across OSS and BSS. Integration ensures that business-facing functions such as order capture connect smoothly with operational functions such as resource provisioning
Q: How does Enterprise Integration reduce complexity?
A: Instead of point-to-point connections, which become unmanageable at scale, Enterprise Integration introduces a structured layer that decouples systems and makes it easier to add, replace or upgrade components without breaking the whole architecture
.
Q: What is Event Management used for?
A: Event Management enables ODA components to communicate using real-time events. Instead of relying on batch jobs or synchronous requests, systems can publish and subscribe to events such as order updates, service degradations or usage records
Q: Is Event Management considered an OSS or BSS function?
A: Event Management is cross-domain. It supports operational use cases such as network fault detection, as well as business use cases such as real-time customer notifications or billing triggers
Q: Why is Event Management important in a modern architecture?
A: Modern digital services require real-time responsiveness. Event-driven integration reduces latency, increases scalability and allows operators to automate responses to issues without manual intervention
.
Q: What is Channel Management used for?
A: Channel Management coordinates how products and services are delivered across physical, digital and partner channels. It ensures that customers have a consistent experience whether they interact via retail, web, mobile, contact centres or third parties
Q: Is Channel Management an OSS or BSS function?
A: Channel Management sits within BSS, as it primarily supports customer engagement and revenue-generating interactions rather than technical service delivery
Q: Why is Channel Management critical for digital transformation?
A: Customers expect seamless journeys across channels. Without centralised channel management, operators risk inconsistent pricing, broken journeys and lost revenue. With ODA, channels are integrated with product catalogues, orders and billing to ensure end-to-end consistency
Q: What challenges does it address for CIOs and architects?
A: It reduces the need for multiple bespoke integrations with front-end systems, provides a reusable capability for omnichannel engagement, and makes it easier to onboard new partner channels quickly
.
Q: What is Content Management used for?
A: Content Management controls digital assets such as documents, multimedia and service descriptions that are required for customer interactions. It supports publishing, versioning and reuse of content across different channels. As cold-calling (push-marketing) is becoming increasingly difficult due to call and email filtering, pull-marketing techniques like content are becoming more important
Q: Is Content Management considered OSS or BSS?
A: Content Management is a BSS capability, as it is closely tied to customer-facing systems such as self-service portals and digital marketing platforms
Q: Why is this relevant to marketing leaders?
A: Consistent content drives accurate product representation, compliance and customer trust. It also helps to establish the company’s narrative and brand. Without it, customers may see conflicting information across channels, leading to lack of service buy-in, churn, complaints or even regulatory risk
.
Q: What is this component used for?
A: Experience Management Strategy & Planning defines the frameworks, KPIs and roadmaps for delivering high-quality customer experiences. It supports the design of customer journeys, service-level expectations and continuous improvement initiatives
Q: Does this belong to OSS or BSS?
A: It is firmly in the BSS domain, as it deals with customer-facing business processes and strategic planning rather than network operations
Q: Why is this component relevant for customer experience leaders?
A: It enables them to move from reactive measurement to proactive design of experiences. With this component, operators can align digital strategy with measurable outcomes such as NPS (Net Promoter Score), churn reduction and upsell rates
.
Q: What is Navigation Management used for?
A: Navigation Management ensures that digital channels such as websites, mobile apps and portals are structured in a way that supports intuitive user journeys. It defines menu structures, page flows and contextual navigation rules
Q: Is this OSS or BSS?
A: Navigation Management is a BSS function because it deals with digital customer-facing applications rather than technical service fulfilment
Q: Why should enterprise architects and product managers care about this component?
A: Poor navigation is one of the most common reasons for abandonment of digital journeys. Navigation Management provides a reusable framework across channels, which improves customer satisfaction and reduces reliance on costly contact centre interactions
.
Q: What is Agreement Management used for?
Agreement Management handles the creation, storage and tracking of agreements such as contracts, SLAs and partner terms. It ensures that obligations and entitlements are applied consistently across the business
Q: Is Agreement Management considered OSS or BSS?
It is a BSS capability because it governs business and customer relationships rather than technical service operations
Q: Why is this important for CIOs and enterprise architects?
It provides a structured way to integrate contracts into customer journeys and operational processes. This ensures automation of entitlements, reduces manual effort and improves compliance
Q: How does it help product managers?
By aligning product offers with contractual commitments, product managers can launch services that meet regulatory and commercial requirements without creating downstream integration challenges
Q: What value does this bring to legal and compliance teams?
It reduces contractual risk by centralising agreements and linking them directly to digital processes, avoiding misalignment between business rules and operational execution
.
Q: What is Bill Generation Management used for?
This component produces accurate and timely bills by combining rated usage, recurring charges and one-off fees. It ensures customers receive clear and compliant statements
Q: OSS or BSS?
Firmly in BSS, as it supports customer billing and financial management
Q: Why is this critical for CFOs and finance teams?
It underpins revenue assurance, ensures compliance with financial regulations and reduces disputes by improving billing transparency
Q: How does this impact customer experience leaders?
Accurate bills are one of the most important trust factors. Poor billing directly drives complaints and churn, so this component has a major effect on NPS and satisfaction scores
Q: Why should CIOs care about this?
Integrating bill generation with digital channels allows customers to access billing in real time, reducing pressure on call centres and improving self-service
.
Q: What is Billing Account Management used for?
This component manages billing accounts, including hierarchies, payment preferences and account relationships across customers and enterprises
Q: OSS or BSS?
BSS, as it supports customer account structures and financial processes
Q: Why is this relevant to enterprise sales leaders?
Large B2B accounts often require complex billing hierarchies. This component allows operators to support group accounts, subsidiaries and consolidated billing without manual workarounds
Q: How does it support CIOs and architects?
It provides a standard model for linking billing accounts to customer records and products, enabling consistency across the architecture
Q: What is the benefit for customer operations managers?
It simplifies billing enquiries and dispute resolution by maintaining a clear structure of accounts, balances and responsibilities
.
Q: What is Billing Inquiries Management used for?
It provides customer service teams and self-service channels with the ability to handle billing questions, disputes and clarifications efficiently
Q: OSS or BSS?
BSS, as it is entirely customer and business facing
Q: Why is this valuable for CX leaders?
Billing issues are one of the top drivers of customer dissatisfaction. This component helps resolve them quickly with clear access to billing data
Q: How does this support call centre managers?
It gives them tools and workflows to resolve billing disputes without requiring manual intervention from back-office teams
Q: Why does this matter for CIOs?
Standardising billing enquiries reduces complexity in CRM and support systems, allowing integration with chatbots, portals and AI-driven support tools
.
Q: What is Debt Collection Management used for?
It automates the processes of identifying overdue balances, sending reminders, negotiating repayment plans and escalating to collections agencies where necessary
Q: OSS or BSS?
BSS, as it deals with customer financial relationships rather than operational service delivery
Q: Why should CFOs care about Debt Collection Management?
It directly impacts cash flow and revenue recovery. Effective debt collection reduces bad debt write-offs while maintaining customer relationships where possible
Q: How is Debt Collection Management relevant for customer experience teams?
Handled poorly, collections damage brand reputation and drive churn. Standardised processes with configurable policies allow firms to balance recovery with customer retention
Q: What is the CIO’s interest in Debt Collection Management?
It ensures collections processes are automated, reducing manual work, ensuring compliance with financial regulations and improving auditability
.
Q: What is Digital Identity Management used for?
It manages secure digital identities for customers, employees and partners, including authentication, authorisation and single sign-on
Q: OSS or BSS?
This is a cross-cutting function but primarily sits within BSS since it manages customer-facing access and entitlements
Q: Why is this important for CIOs?
It reduces security risks, supports compliance with privacy regulations and allows for consistent identity management across systems
Q: How does this support CX leaders?
It enables seamless login experiences across channels, reducing friction and abandonment in digital journeys
Q: Why should compliance officers care?
Strong identity management ensures GDPR and data protection requirements are met, reducing risk of breaches and fines
.
Q: What is Document Management used for?
It stores, retrieves and manages documents such as contracts, invoices and compliance records linked to customers and partners
Q: OSS or BSS?
Firmly BSS, since it manages business records and customer documents rather than technical operations
Q: Why is this important for customer service managers?
It gives them quick access to relevant documents when resolving customer queries, improving first-contact resolution
Q: How does it support legal and compliance teams?
It ensures accurate document retention and auditability for regulatory requirements
Q: Why would CIOs care about this?
Standardised document management reduces duplication across systems and enables integration with self-service channels
.
Q: What is this component used for?
It tracks and manages sales leads and opportunities, supporting pipeline management and conversion tracking
Q: OSS or BSS?
BSS, since it is focused on sales and revenue growth functions
Q: Why is this critical for sales leaders?
It improves visibility of the sales pipeline, supports forecasting and helps identify the highest-value opportunities
Q: How does this benefit product managers?
It links lead data with product demand, helping refine offers and pricing strategies
Q: Why would CIOs prioritise this?
Standardised lead and opportunity management reduces reliance on siloed CRM tools and aligns sales data with other BSS systems
.
Q: What is Marketing Communications used for?
It manages campaigns, promotions and targeted communications across digital and physical channels
Q: OSS or BSS?
BSS, since it is focused on customer engagement and revenue generation
Q: Why is this valuable for CMOs and marketing leaders?
It provides a consistent way to deliver targeted communications, improving conversion rates and reducing wasted spend
Q: How does this support CX leaders?
It ensures that customers receive relevant and consistent messages, improving personalisation and reducing churn
Q: Why would CIOs care?
It reduces the need for multiple, disconnected marketing tools and ensures that campaigns can be integrated with product catalogues and order systems
.
Q: What is this component used for?
It records and manages interactions between parties, whether customer, partner or employee, across all channels
Q: OSS or BSS?
BSS, as it handles engagement and interaction rather than operational delivery
Q: Why is this relevant for customer service managers?
It gives a 360-degree view of customer interactions, reducing repeat queries and improving issue resolution
Q: Why should CIOs and architects care?
It provides a standard model for capturing and integrating interactions across systems, reducing fragmentation
Q: How does this support product and marketing teams?
It provides insights into customer behaviours and preferences, informing product development and campaign design
.
Q: What is Party Management used for?
It manages information about all parties, including individuals, organisations and partners, ensuring accurate and consistent records
Q: OSS or BSS?
BSS, as it is central to customer and partner relationship management
Q: Why is this critical for CIOs?
It provides a master record for all parties, reducing duplication and data quality issues across systems
Q: How does this support compliance officers?
It ensures accurate party data is maintained, supporting KYC (know your customer) and regulatory requirements
Q: Why should product managers care?
It enables consistent and reliable customer data to be linked with offers, reducing failed transactions and service issues
.
Q: What is this component used for?
It manages customer privacy preferences, consents and data-sharing rules in line with regulations such as GDPR
Q: OSS or BSS?
BSS, as it governs customer-facing processes around privacy and consent
Q: Why is this essential for compliance officers?
It ensures regulatory compliance by providing traceable records of consents and data use
Q: How does this support CX leaders?
By giving customers transparency and control over their data, it builds trust and reduces churn risk
Q: Why should CIOs and architects prioritise this?
It provides a standardised approach to privacy across multiple systems, reducing complexity and compliance costs
.
Q: What is Party Problem Management used for?
It tracks and resolves customer problems related to services, billing or interactions, complementing technical fault management
Q: OSS or BSS?
BSS, since it is customer-facing rather than network-focused
Q: Why is this important for customer operations managers?
It provides structured workflows for resolving issues, improving resolution times and customer satisfaction
Q: How does this support CIOs?
It aligns with CRM and support platforms, reducing duplication and ensuring consistent handling of customer issues
Q: Why should CX leaders care?
It enables proactive management of problems, reducing churn caused by unresolved issues
.
Q: What is Payment Management used for?
It handles payment processing, including integration with banks, gateways and third-party payment providers
Q: OSS or BSS?
BSS, as it is focused on revenue collection
Q: Why is this important for CFOs?
It provides reliable cash flow management, reduces failed transactions and supports multiple payment methods
Q: Why would CIOs care?
It reduces the complexity of payment integrations by centralising them into a reusable component
Q: How does this impact customer experience leaders?
It enables smooth, real-time payment experiences across channels, which directly impacts trust and satisfaction
.
Q: What is this component used for?
It defines and manages roles and permissions for parties, ensuring secure access to systems and services
Q: OSS or BSS?
Cross-cutting, but typically BSS given its focus on business and customer-facing processes
Q: Why is this important for CIOs?
It enforces security and governance across applications, reducing unauthorised access and risk
Q: How does this support compliance officers?
It ensures clear audit trails of who has access to what, which is critical for regulatory compliance
Q: Why should enterprise architects value this?
It provides a consistent model for role and permission assignment across systems, reducing integration challenges
.
Q: What is Sales Strategy & Planning used for?
It defines and manages sales strategies, targets and planning processes to align teams and maximise revenue growth
Q: OSS or BSS?
BSS, as it is focused on sales and commercial planning
Q: Why is this important for sales leaders?
It provides a structured framework for setting and tracking sales goals, improving accountability and performance
Q: How does this support product managers?
It links sales strategies with product launches, ensuring go-to-market activities are aligned and measurable
Q: Why would CIOs and architects care?
It integrates sales planning with wider BSS systems, reducing silos and enabling accurate performance tracking
.
Q: What is Agreement Management used for?
Agreement Management is used to create, maintain and monitor contracts, agreements, service-level terms and partnership arrangements. This ensures that all obligations, entitlements and commercial terms are enforced consistently across business processes. It reduces the risk of misinterpretation, automates entitlement validation and makes it easier for operators to align service delivery with contractual promises
Q: Is Agreement Management an OSS or BSS function?
Agreement Management is a BSS function. It deals with commercial arrangements, legal compliance and customer or partner-facing processes. Unlike OSS components, which manage service or network operations, Agreement Management is about governing the business relationship layer and ensuring commercial consistency
Q: Why is Agreement Management important for CIOs and enterprise architects?
For CIOs and architects, Agreement Management ensures that contracts and SLAs can be directly embedded into IT workflows. This prevents manual errors, enables automation of entitlement checks, and provides a reliable framework for integrating contract data into order management, billing and assurance processes
Q: How does Agreement Management help product managers?
Product managers benefit because the component ensures that new product launches respect existing contractual terms. This prevents issues such as promising service levels that exceed agreed commitments or pricing that breaches contractual rules. It makes product launches faster and less risky
Q: What value does Agreement Management bring to legal and compliance teams?
Legal and compliance teams gain a centralised view of all agreements with audit trails and linkage to operational systems. This reduces regulatory risk and ensures contracts are enforced as written, instead of relying on ad-hoc interpretation across departments
.
Q: What is Bill Generation Management used for?
Bill Generation Management is responsible for producing clear, accurate and timely bills. It brings together rated usage events, recurring charges, discounts and one-off items into a single statement. By ensuring bills are reliable, it supports both customer satisfaction and revenue assurance, reducing disputes and costly manual rework
Q: Is Bill Generation Management an OSS or BSS function?
Bill Generation Management is a BSS function. It directly supports financial processes and customer interactions related to invoicing. While OSS systems capture service usage, the actual calculation, formatting and issuing of bills sits firmly within BSS
Q: Why is Bill Generation Management critical for CFOs and finance leaders?
For CFOs, this component is critical because billing accuracy underpins both revenue assurance and regulatory compliance. Even small billing errors can result in significant financial leakage or reputational damage. Automated, rules-based bill generation ensures consistency and reduces operational costs associated with disputes
Q: How does Bill Generation Management impact customer experience leaders?
Accurate billing is one of the strongest drivers of trust in a telecom provider. If customers cannot trust their bills, satisfaction and NPS scores fall rapidly. Bill Generation Management gives CX leaders confidence that customer interactions will not be undermined by billing disputes
Q: Why should CIOs prioritise Bill Generation Management?
CIOs should care because integration between billing and digital channels enables customers to view and query bills in real time through apps and portals. This reduces support calls, improves transparency and builds customer confidence in digital self-service journeys
.
Q: What is Billing Account Management used for?
Billing Account Management controls how customer accounts are structured for invoicing, payment and financial reporting. It manages hierarchies, preferences, account relationships and ownership. This is especially important in enterprise scenarios, where customers often need consolidated bills for groups or subsidiaries
Q: Is Billing Account Management an OSS or BSS function?
Billing Account Management is a BSS function. It sits firmly in the business-facing layer, handling financial account data and relationships. OSS systems focus on operational elements such as resources and services, but the management of accounts belongs to BSS
Q: Why is Billing Account Management valuable for enterprise sales leaders?
Sales leaders rely on this component to support complex enterprise arrangements, such as global account hierarchies or parent-subsidiary billing. By enabling flexible account structures, it removes a major barrier to winning and retaining large enterprise customers
Q: How does Billing Account Management support CIOs and enterprise architects?
For CIOs and architects, it provides a consistent data model that links billing accounts with customer records and product entitlements. This ensures that data flows correctly between CRM, billing and financial reporting systems, reducing errors and manual workarounds
Q: What is the benefit of Billing Account Management for customer operations managers?
Customer operations teams benefit because enquiries, adjustments and disputes are easier to handle when accounts are structured consistently. Instead of navigating multiple fragmented systems, staff can quickly see relationships and responsibilities across accounts
.
Q: What is Billing Inquiries Management used for?
Billing Inquiries Management provides customer service teams and digital channels with the ability to address billing-related questions, disputes and clarifications. It ensures that customers receive clear, prompt answers, reducing frustration and improving retention
Q: Is Billing Inquiries Management an OSS or BSS function?
Billing Inquiries Management is a BSS function. It is part of the customer-facing business support layer, providing processes and tools for managing financial and billing queries rather than technical service issues
Q: Why is Billing Inquiries Management important for CX leaders?
CX leaders view billing enquiries as a critical pain point. If customers cannot easily resolve billing concerns, trust declines quickly. This component provides structured processes and access to billing data that help resolve disputes on first contact, improving satisfaction
Q: How does Billing Inquiries Management support call centre managers?
For call centre managers, it provides workflows, data access and escalation paths so agents can resolve issues without transferring calls or involving back-office teams. This reduces average handling time and improves operational efficiency
Q: Why should CIOs and digital transformation leaders care about Billing Inquiries Management?
CIOs care because standardising inquiry handling allows integration with digital channels such as self-service portals, chatbots and AI assistants. This supports automation, reduces call volumes and delivers a better digital-first customer experience
.
Q: What is Debt Collection Management used for?
Debt Collection Management automates the processes for identifying overdue balances, notifying customers, managing repayment plans and escalating unpaid amounts to collections teams or agencies. It ensures consistent, compliant and efficient recovery of outstanding debt, while balancing customer retention and financial recovery goals
Q: Is Debt Collection Management an OSS or BSS function?
Debt Collection Management is a BSS function, as it supports financial and customer-facing processes rather than operational service management. It sits within the commercial layer of the architecture and directly impacts revenue recovery and financial health
Q: Why is Debt Collection Management important for CFOs and finance leaders?
CFOs rely on this component to safeguard cash flow, reduce bad debt write-offs and ensure compliance with accounting standards. By automating recovery processes, it reduces operational costs and improves recovery rates without relying on inconsistent manual approaches
Q: How does Debt Collection Management support customer experience leaders?
Handled poorly, collections can damage trust and drive churn. By managing repayment options and tailoring communications, this component helps balance recovery with customer experience, ensuring that sensitive financial situations do not undermine long-term relationships
Q: Why should CIOs and enterprise architects care about Debt Collection Management?
CIOs value this component because it integrates seamlessly with billing, payment and CRM systems, ensuring that debt recovery processes are automated, auditable and consistent across multiple customer touchpoints. This reduces system complexity and compliance risk
.
Q: What is Digital Identity Management used for?
Digital Identity Management governs the creation, authentication and authorisation of digital identities for customers, employees and partners. It enables secure login, single sign-on, and role-based access to systems and services. This provides the foundation for secure digital interactions in a connected ecosystem
Q: Is Digital Identity Management an OSS or BSS function?
Digital Identity Management is primarily a BSS function, although it has cross-cutting value across the entire architecture. It manages access for customer-facing services and business processes, ensuring that identities are secure and permissions are correctly applied
Q: Why is Digital Identity Management important for CIOs?
For CIOs, this component reduces security risks by enforcing consistent authentication and access control policies across systems. It also helps with regulatory compliance and simplifies the integration of identity services across multiple platforms and vendors
Q: How does Digital Identity Management improve customer experience?
Customers expect seamless and secure login across multiple channels. By supporting single sign-on and federated identity, this component reduces friction in customer journeys while maintaining strong protection of personal data
Q: Why is Digital Identity Management essential for compliance officers?
It provides audit trails and clear consent records, supporting GDPR and other privacy regulations. This helps organisations demonstrate that only authorised individuals have access to sensitive systems and data
.
Q: What is Document Management used for?
Document Management provides a structured way to store, retrieve, version and manage documents related to customer and business operations. This includes contracts, invoices, technical records and compliance documentation. It ensures documents are secure, accessible and consistent across the organisation
Q: Is Document Management an OSS or BSS function?
Document Management is a BSS function, as it primarily supports customer and business-facing processes. While OSS systems may generate technical reports, the structured management of business documents is firmly in the BSS domain
Q: Why is Document Management valuable for customer service managers?
It allows service teams to access the right documents quickly when resolving customer queries, reducing resolution times and improving customer satisfaction. This avoids the frustration caused by missing or duplicated records
Q: How does Document Management support compliance officers and legal teams?
It ensures that records are stored securely, retained for the required period and easily retrievable for audits or regulatory checks. This reduces the risk of non-compliance and legal disputes
Q: Why should CIOs and architects care about Document Management?
For CIOs, standardised document management reduces duplication across systems and makes it easier to integrate documents into self-service portals, enabling customers to access their own records without human intervention
.
Q: What is Lead & Opportunity Management used for?
Lead & Opportunity Management tracks the lifecycle of potential sales opportunities, from initial interest through qualification to closure. It provides sales teams with structured pipelines, helps prioritise leads and improves forecasting accuracy. This supports both B2C and B2B sales strategies
Q: Is Lead & Opportunity Management an OSS or BSS function?
Lead & Opportunity Management is a BSS function, as it focuses on business development, sales and revenue growth. It does not manage operational delivery but instead supports commercial outcomes
Q: Why is Lead & Opportunity Management critical for sales leaders?
Sales leaders use this component to manage pipelines and identify high-value opportunities. It provides visibility into performance, improves accountability and supports better sales forecasting
Q: How does Lead & Opportunity Management support product managers?
It links lead and opportunity data to product demand, giving product managers insights into which offerings resonate with customers. This allows them to refine pricing and features to meet real-world demand
Q: Why would CIOs and architects care about Lead & Opportunity Management?
This component ensures that sales pipelines are integrated with CRM and order management systems, reducing reliance on siloed tools. This standardisation makes it easier to share sales data across the organisation and align it with operational delivery
.
Q: What is Marketing Communications used for?
Marketing Communications manages the planning, execution and delivery of promotional messages, campaigns and customer communications across digital and physical channels. It ensures that communications are consistent, targeted and aligned with customer profiles, reducing the risk of duplication or irrelevant messaging
Q: Is Marketing Communications an OSS or BSS function?
Marketing Communications is a BSS function. It directly supports customer engagement, brand promotion and sales activities, which are all business-facing. Unlike OSS functions that deal with service and network delivery, this component focuses on creating demand and maintaining relationships with customers
Q: Why is Marketing Communications important for CMOs and marketing leaders?
For marketing leaders, this component provides the tools to design and execute integrated campaigns across multiple touchpoints. It ensures campaigns are consistent, measurable and aligned with strategic goals, improving return on marketing investment and reducing wasted spend
Q: How does Marketing Communications support CX leaders?
It helps deliver the right message at the right time to the right customer. This strengthens personalisation and avoids the frustration caused by irrelevant or conflicting communications, which can damage customer trust and lead to churn
Q: Why should CIOs and architects care about Marketing Communications?
CIOs value this component because it reduces the need for fragmented marketing systems and ensures that campaign data can be integrated with customer, product and order systems. This improves alignment between marketing efforts and actual service delivery
.
Q: What is Party Interaction Management used for?
Party Interaction Management records, tracks and manages every interaction that takes place between the organisation and its customers, partners or employees. It captures details across multiple channels, including calls, digital chats, in-person meetings and automated interactions, providing a single history of engagement
Q: Is Party Interaction Management an OSS or BSS function?
Party Interaction Management is a BSS function. It focuses on customer and partner engagement rather than technical service delivery. It ensures consistency of experience and understanding across the business
Q: Why is Party Interaction Management important for CX leaders?
CX leaders rely on this component to provide a 360-degree view of the customer. By consolidating all interactions, it prevents repeat queries, reduces frustration and ensures that customers are not asked to repeat information multiple times
Q: Why should CIOs and enterprise architects care about Party Interaction Management?
This component provides a standardised way to capture and share interaction data across systems. By avoiding siloed records, it reduces integration challenges and ensures consistency across CRM, support and digital platforms
Q: How does Party Interaction Management support product and marketing teams?
It generates insights into customer behaviour and preferences, which can inform product development and targeted campaigns. This ensures that offerings are aligned with what customers actually want and how they interact with the business
.
Q: What is Party Management used for?
Party Management is responsible for maintaining accurate and consistent records of all parties the organisation interacts with. This includes individuals, organisations, households and partners. It provides the foundation for customer, partner and enterprise data across the business, enabling effective engagement and service delivery
Q: Is Party Management an OSS or BSS function?
Party Management is a BSS function. It is focused on the business-facing aspect of managing customers and partners, rather than managing services or technical resources which sit within OSS
Q: Why is Party Management critical for CIOs and enterprise architects?
CIOs and architects see this as a core master data management capability. It ensures that there is a single source of truth for party information across systems, reducing duplication and preventing errors caused by inconsistent data
Q: How does Party Management support compliance officers?
It enables regulatory compliance by ensuring customer and partner records are accurate, complete and up to date. This supports obligations such as KYC (know your customer) and data retention rules
Q: Why should product managers and commercial teams care about Party Management?
Reliable party data ensures that offers are applied correctly and that customers are billed, contacted and supported without errors. It also supports segmentation and targeting, which are essential for launching new services effectively
.
Q: What is Party Privacy Management used for?
Party Privacy Management governs the way customer data is collected, stored and shared. It manages consent records, privacy preferences and data access rules. It ensures that customer choices are respected and that the business complies with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA
Q: Is Party Privacy Management an OSS or BSS function?
Party Privacy Management is a BSS function. It focuses on the business and customer-facing aspects of privacy and consent, ensuring that data is handled properly throughout commercial and operational processes
Q: Why is Party Privacy Management essential for compliance officers?
Compliance teams rely on this component to maintain auditable consent records and data access logs. It reduces the risk of regulatory penalties by ensuring that customer data is only processed in line with agreed preferences and legal requirements
Q: How does Party Privacy Management support CX leaders?
It builds trust with customers by giving them visibility and control over their personal data. When customers feel their data is handled transparently, they are more likely to remain loyal and engage with new services
Q: Why should CIOs and architects prioritise Party Privacy Management?
It provides a standardised approach to privacy across multiple systems and vendors. By centralising privacy management, it reduces the complexity and cost of compliance, while ensuring that customer data is managed consistently
.
Q: What is Party Problem Management used for?
Party Problem Management manages the identification, tracking and resolution of customer problems. Unlike technical fault management, which deals with network or service issues, this component focuses on customer-facing problems such as incorrect bills, failed orders or service quality complaints. It provides workflows and escalation paths to ensure that problems are resolved efficiently and consistently
Q: Is Party Problem Management an OSS or BSS function?
Party Problem Management is a BSS function. It sits within the customer engagement and support layer of the business, focusing on resolving customer-facing problems rather than managing technical resources, which is the role of OSS components
Q: Why is Party Problem Management important for customer operations managers?
Customer operations managers use this component to standardise how problems are logged and resolved. It reduces manual effort, ensures consistent handling of complaints and improves service quality by giving visibility into common issues across the customer base
Q: How does Party Problem Management support CIOs and enterprise architects?
For CIOs, this component integrates with CRM, billing and service management systems to create a closed-loop process. This reduces duplication of effort, improves data accuracy and ensures that customer problems are linked to the right operational systems for resolution
Q: Why should CX leaders care about Party Problem Management?
CX leaders value this component because it reduces customer frustration by improving resolution times. Proactive problem management also helps to identify and address recurring issues, improving trust and reducing churn
.
Q: What is Payment Management used for?
Payment Management handles the collection and processing of payments through multiple channels, including credit cards, direct debit, bank transfers and third-party gateways. It ensures that payments are validated, reconciled and recorded accurately, supporting both customer satisfaction and financial integrity
Q: Is Payment Management an OSS or BSS function?
Payment Management is a BSS function. It directly supports revenue collection and customer financial interactions. While OSS components manage technical service fulfilment, Payment Management focuses on ensuring money is collected securely and efficiently
Q: Why is Payment Management important for CFOs and finance leaders?
For CFOs, this component is critical for maintaining cash flow and reducing revenue leakage. It enables multiple payment options, improves reconciliation processes and supports compliance with financial regulations, ensuring accurate reporting and transparency
Q: How does Payment Management improve customer experience?
Smooth payment processes directly affect customer satisfaction. Failed or delayed payments can create frustration and trust issues. By supporting multiple payment methods and real-time validation, this component reduces friction and enhances digital self-service journeys
Q: Why should CIOs and architects care about Payment Management?
CIOs value this component because it centralises payment processing, reducing the need for multiple integrations with external providers. This makes it easier to add new payment methods and maintain compliance across all channels
.
Q: What is Party Roles & Permissions Management used for?
Party Roles & Permissions Management defines and enforces the roles and access permissions for different parties, including customers, employees and partners. It ensures that only authorised individuals can access specific data, systems or services, reducing risk and maintaining governance
Q: Is Party Roles & Permissions Management an OSS or BSS function?
Party Roles & Permissions Management is primarily a BSS function, although it has value across both business and operational systems. It governs business-facing access policies while ensuring consistency in technical environments where needed
Q: Why is Party Roles & Permissions Management important for CIOs?
For CIOs, this component is vital for enforcing security and access control across a complex IT landscape. It reduces unauthorised access, improves governance and simplifies audit processes by providing a centralised system for managing roles and permissions
Q: How does Party Roles & Permissions Management support compliance officers?
Compliance officers rely on this component to demonstrate that access to sensitive systems and data is properly controlled. It provides full audit trails and ensures that roles and permissions are aligned with legal and regulatory requirements
Q: Why should enterprise architects care about Party Roles & Permissions Management?
Enterprise architects benefit from a standardised model for role and permission assignment across multiple systems. This reduces integration complexity, supports consistency across vendors and simplifies governance at scale
.
Q: What is Sales Strategy & Planning used for?
Sales Strategy & Planning provides the structure for setting sales objectives, designing go-to-market strategies and tracking progress against targets. It helps align sales activities with corporate objectives, product launches and market opportunities, ensuring that teams are working towards shared goals
Q: Is Sales Strategy & Planning an OSS or BSS function?
Sales Strategy & Planning is a BSS function. It is focused on commercial and business outcomes rather than technical service operations, making it a core part of the business support layer
Q: Why is Sales Strategy & Planning important for sales leaders?
Sales leaders rely on this component to create structured, measurable plans that guide their teams. It provides visibility into performance, helps track progress against goals and ensures accountability across sales functions
Q: How does Sales Strategy & Planning support product managers?
For product managers, this component ensures that new products and services are launched with clear sales plans, targets and enablement strategies. This alignment increases the chances of successful adoption and revenue growth
Q: Why should CIOs and enterprise architects care about Sales Strategy & Planning?
CIOs and architects value this component because it integrates sales planning with other BSS systems such as product catalogues, CRM and performance management. This ensures that planning is data-driven, consistent and aligned across the business
.
Q: What is Bill Calculation used for?
Bill Calculation is responsible for applying pricing rules, discounts, allowances and usage ratings to generate accurate charge details before they are passed to the billing system. It ensures that customers are billed correctly for the products and services they use, whether consumption-based, subscription or bundled
Q: Is Bill Calculation an OSS or BSS function?
Bill Calculation is a BSS function. It is part of the financial and customer-facing support layer, working closely with billing and account management systems. OSS systems may provide usage data, but the calculation of charges based on tariffs and rules is handled within BSS
Q: Why is Bill Calculation important for CFOs and finance leaders?
CFOs depend on this component to ensure that all usage and product charges are applied correctly, avoiding revenue leakage. Even small errors in calculation logic can lead to significant financial losses at scale. Bill Calculation provides the consistency and auditability needed to protect revenue streams
Q: How does Bill Calculation impact customer experience leaders?
Customers expect transparency and fairness in billing. Bill Calculation ensures accuracy in applying discounts, promotions and usage thresholds, reducing the likelihood of billing disputes and improving trust. This directly impacts customer satisfaction and loyalty
Q: Why should CIOs and enterprise architects care about Bill Calculation?
CIOs and architects value this component because it centralises pricing and rating logic, avoiding duplication across multiple systems. This makes it easier to update tariffs, introduce new offers and integrate with digital channels that need real-time pricing information
.
Q: What is Commission Management used for?
Commission Management calculates, tracks and pays commissions to internal sales teams, resellers and partners. It manages commission structures, performance thresholds and incentive schemes, ensuring that compensation is fair, transparent and aligned with business goals
Q: Is Commission Management an OSS or BSS function?
Commission Management is a BSS function. It directly relates to commercial processes, partner management and sales operations. OSS systems are not involved, as this is about financial recognition of sales performance rather than service delivery
Q: Why is Commission Management important for sales leaders?
Sales leaders use this component to motivate teams and ensure transparency in incentives. Clear, accurate commission management reduces disputes, improves morale and helps align behaviours with strategic objectives
Q: How does Commission Management support CFOs and finance teams?
For finance teams, it provides visibility into commission liabilities, ensures compliance with financial reporting standards and avoids overpayment errors. It also helps balance incentive structures against profitability targets
Q: Why should CIOs and architects care about Commission Management?
CIOs see value in integrating this component with CRM and billing systems so that commissions are tied directly to confirmed sales and revenue. This reduces manual reconciliation and increases confidence in reporting
.
Q: What is Product Assurance Management used for?
Product Assurance Management ensures that products and services perform as promised and meet customer expectations. It validates that product features, SLAs and quality levels are consistently delivered, and provides monitoring and reporting to identify gaps or issues
Q: Is Product Assurance Management an OSS or BSS function?
Product Assurance Management is a hybrid, spanning both OSS and BSS. It is rooted in BSS because it monitors customer-facing product commitments, but it must also interact with OSS to validate technical service quality. It acts as the bridge between commercial promises and operational delivery
Q: Why is Product Assurance Management important for CX leaders?
CX leaders value this component because it ensures that what customers experience matches what was promised during sales. It helps track service-level compliance, reducing complaints and improving retention
Q: How does Product Assurance Management support product managers?
Product managers benefit by having feedback on how products are performing in practice. This allows them to refine features, pricing and promotions based on real-world delivery and customer outcomes
Q: Why should CIOs and architects care about Product Assurance Management?
For CIOs and architects, this component provides a structured way to connect commercial product definitions with operational performance data. It reduces the gap between marketing promises and technical delivery, ensuring alignment across OSS and BSS
.
Q: What is Product Catalogue Management used for?
Product Catalogue Management provides a centralised repository of all products and services offered by the organisation. It defines product structures, attributes, rules, dependencies and relationships, enabling consistent use across sales, ordering, billing and support systems. It is the foundation for product lifecycle management
Q: Is Product Catalogue Management an OSS or BSS function?
Product Catalogue Management is a BSS function. It manages the business-facing representation of products rather than the technical resources that deliver them. However, it often integrates with OSS catalogues to ensure that commercial offerings map accurately to technical capabilities
Q: Why is Product Catalogue Management important for CIOs and enterprise architects?
This component is critical for CIOs because it centralises product definitions, eliminating duplication across siloed systems. It ensures that all business processes reference the same product data, reducing errors and speeding up new product launches
Q: How does Product Catalogue Management support product managers?
Product managers use this component to design and configure new offerings. It provides flexibility to define bundles, add-ons and pricing models, supporting rapid innovation without heavy IT rework
Q: Why is Product Catalogue Management essential for sales and marketing leaders?
Sales and marketing teams rely on the product catalogue to ensure consistent communication of product features, pricing and availability across all channels. A central catalogue ensures customers see the same offer regardless of how or where they engage
.
Q: What is Product Configurator used for?
Product Configurator allows customers, partners and sales teams to customise products and bundles according to defined rules and constraints. It ensures that configurations are valid, technically feasible and commercially viable. This is critical for complex offerings such as enterprise connectivity, converged services or multi-play bundles
Q: Is Product Configurator an OSS or BSS function?
Product Configurator is a BSS function. It sits within the business layer of customer engagement and commerce, enabling configuration at the point of sale or service request. While it must align with OSS capabilities, its focus is on guiding commercial choices and preventing invalid orders
Q: Why is Product Configurator important for product managers?
Product managers use this component to ensure that complex products can be sold consistently and accurately. By embedding business rules, they can launch offers that are flexible but still aligned with technical and financial constraints
Q: How does Product Configurator support sales leaders and account managers?
Sales teams benefit by being able to offer tailored solutions to customers without relying on manual validation or back-office intervention. This reduces order fallout and shortens the sales cycle, improving win rates and customer satisfaction
Q: Why should CIOs and enterprise architects care about Product Configurator?
CIOs see value in integrating configuration logic across catalogues, ordering and billing systems. This ensures that customer choices flow through the architecture without errors, reducing costly rework and failed activations
.
Q: What is Product Inventory used for?
Product Inventory tracks all products and services that have been sold or activated, maintaining a real-time record of their status and attributes. It enables operators to see which products are active for each customer, ensuring accurate billing, service management and support
Q: Is Product Inventory an OSS or BSS function?
Product Inventory is a BSS function. It provides the customer-facing view of what products are owned and in use. It often integrates with Service Inventory and Resource Inventory in OSS to ensure alignment between what is promised to customers and what is technically delivered
Q: Why is Product Inventory important for CIOs and enterprise architects?
For CIOs, Product Inventory provides a single source of truth for active products across the organisation. This reduces duplication, ensures data accuracy and improves alignment between commercial systems and operational platforms
Q: How does Product Inventory support customer operations managers?
It allows customer service teams to quickly verify what products a customer has, their current status and any entitlements. This improves resolution of service issues and billing disputes
Q: Why should product managers care about Product Inventory?
Product managers rely on accurate inventory data to analyse product performance, adoption rates and lifecycle status. This supports decisions about when to retire, enhance or bundle existing products
.
Q: What is Product Order Capture & Validation used for?
Product Order Capture & Validation is responsible for receiving customer orders, validating them against business rules and checking feasibility before processing. It ensures that orders are complete, accurate and ready to move forward to fulfilment without manual intervention
Q: Is Product Order Capture & Validation an OSS or BSS function?
It is a BSS function. It sits at the customer-facing front end of the ordering process. While it interacts with OSS systems to check technical feasibility, its core responsibility is business validation and preparation for fulfilment
Q: Why is Product Order Capture & Validation important for CX leaders?
This component ensures customers experience smooth and error-free ordering journeys. Orders that fail validation cause delays, frustration and cancellations. By capturing and validating upfront, customers get a better first-time-right experience
Q: How does Product Order Capture & Validation support CIOs and architects?
CIOs benefit from standardised order capture and validation because it reduces the need for manual checks and workarounds. This creates a consistent process that integrates across catalogues, billing and fulfilment systems
Q: Why is Product Order Capture & Validation essential for sales teams?
It ensures that sales staff can confidently take orders without worrying about whether they are technically or commercially valid. This reduces order fallout, improves closure rates and enhances customer trust in the sales process
.
Q: What is Product Order Delivery Orchestration & Management used for?
This component manages the end-to-end orchestration of product order fulfilment. Once an order is captured and validated, it breaks down the request into service and resource orders, coordinates dependencies and tracks progress until delivery is complete. It ensures that customer orders are fulfilled accurately, on time and in the correct sequence
Q: Is Product Order Delivery Orchestration & Management an OSS or BSS function?
It is a hybrid, with a strong BSS focus. The orchestration begins in the BSS layer, coordinating with OSS fulfilment functions. Its role is to ensure that commercial orders are successfully translated into operational actions across networks and IT systems
Q: Why is Product Order Delivery Orchestration & Management important for CIOs?
For CIOs, this component is critical because it eliminates manual handovers between business and technical teams. It provides end-to-end visibility of order fulfilment, reduces errors and ensures customers receive services faster
Q: How does Product Order Delivery Orchestration & Management support CX leaders?
It directly affects the customer experience by ensuring orders are delivered on time and without errors. By providing real-time tracking of progress, it also enables proactive communication with customers about their order status
Q: Why should enterprise architects value Product Order Delivery Orchestration & Management?
Enterprise architects benefit because this component provides a structured, modular orchestration process. This reduces complexity, supports multi-vendor integration and ensures that future services can be introduced quickly without redesigning fulfilment flows
.
Q: What is Product Test Management used for?
Product Test Management ensures that new or updated products are properly tested before being launched to customers. It provides frameworks and processes for validating functionality, pricing, ordering and delivery. This reduces the risk of failures in production and ensures that products meet customer expectations before they go live
Q: Is Product Test Management an OSS or BSS function?
Product Test Management is primarily a BSS function. It validates products from the commercial and customer perspective, although it often integrates with OSS test environments to check feasibility and delivery capability. Its main role is to ensure readiness from a business and customer engagement perspective
Q: Why is Product Test Management important for product managers?
Product managers rely on this component to reduce the risk of failed launches. By validating products against business rules and customer journeys, they can ensure offerings are market-ready and avoid costly fixes after launch
Q: How does Product Test Management support CIOs and enterprise architects?
CIOs and architects benefit because this component introduces structured testing processes that are integrated into the broader product lifecycle. This reduces reliance on ad hoc testing and ensures new services can be introduced consistently at scale
Q: Why should CX leaders care about Product Test Management?
Testing products from a customer perspective ensures that experiences are smooth, pricing is correct and fulfilment works as expected. This directly improves satisfaction and reduces complaints after launch
.
Q: What is Product Usage Management used for?
Product Usage Management collects, records and monitors product usage data for billing, reporting and analytics. It ensures that usage events such as calls, data sessions or digital transactions are correctly attributed to the right customer and product, and that usage limits, thresholds or bundles are enforced
Q: Is Product Usage Management an OSS or BSS function?
Product Usage Management is a BSS function, although it consumes usage data from OSS and network systems. It applies this data in a business context, ensuring it is linked correctly to products, accounts and billing processes
Q: Why is Product Usage Management important for CFOs and finance leaders?
Accurate usage management prevents revenue leakage and supports reliable billing. For CFOs, it ensures that every unit of consumption is properly captured and charged according to the customer’s contract or tariff plan
Q: How does Product Usage Management support CIOs?
CIOs value this component because it provides a standardised way to process usage across products, reducing duplication and integration complexity. It ensures that usage data flows seamlessly into billing, analytics and customer engagement systems
Q: Why should customer experience leaders care about Product Usage Management?
Real-time usage management enables customers to see their consumption through apps or portals. This transparency builds trust, reduces bill shock and empowers customers to manage their usage more effectively
.
Q: What is Purchase Management used for?
Purchase Management supports the buying of goods and services by the organisation, including procurement from suppliers and partners. It covers supplier management, order processing, approvals and financial reconciliation. This ensures that operators can source products and services efficiently while maintaining compliance and cost control
Q: Is Purchase Management an OSS or BSS function?
Purchase Management is a BSS function. It operates within the financial and supplier-facing business processes of the organisation rather than in the technical domain of OSS
Q: Why is Purchase Management important for CFOs and procurement leaders?
It improves visibility and control over procurement spend, reduces errors in purchasing and ensures compliance with procurement policies. For CFOs, this directly impacts profitability by controlling costs and improving financial governance
Q: How does Purchase Management support CIOs and architects?
CIOs value the standardisation this component brings, particularly in integrating procurement processes with financial and supplier management systems. This reduces duplication, ensures consistent workflows and provides a clear audit trail
Q: Why should operations managers care about Purchase Management?
It improves efficiency by automating purchase workflows, approvals and supplier interactions. This reduces manual work and accelerates time-to-value for sourcing goods and services
.
Q: What is Fault Management used for?
Fault Management detects, logs and manages faults in network, IT and service infrastructures. It identifies problems through alarms, notifications and monitoring data, then triggers workflows for resolution. This ensures that faults are identified quickly and resolved before they impact customers
Q: Is Fault Management an OSS or BSS function?
Fault Management is an OSS function. It is focused on operational monitoring and recovery of technical infrastructure, ensuring continuity of service. While its outcomes influence customer experience, its scope is firmly within operational management
Q: Why is Fault Management important for CIOs and operations leaders?
It provides the foundation for network reliability and service availability. Without effective fault management, outages can persist unnoticed, leading to revenue loss, reputational damage and regulatory breaches. CIOs rely on this component to maintain operational resilience
Q: How does Fault Management support customer experience leaders?
Although customers do not see this function directly, its impact is felt in service uptime and reliability. By reducing downtime and accelerating resolution, it protects customer satisfaction and prevents churn caused by service interruptions
Q: Why should enterprise architects value Fault Management?
Enterprise architects rely on this component as part of an integrated assurance framework. It provides standardised fault data that can be correlated with performance and usage information, giving a holistic view of service health
.
Q: What is IT and Network Infrastructure Management used for?
This component manages the physical and virtual infrastructure that underpins services, including data centres, cloud environments, transport networks and access networks. It provides visibility, monitoring and lifecycle management of infrastructure assets, ensuring they are secure, available and efficient
Q: Is IT and Network Infrastructure Management an OSS or BSS function?
It is an OSS function. It operates within the domain of technical resource management, ensuring infrastructure can deliver the services promised by the business. Its focus is operational rather than commercial
Q: Why is IT and Network Infrastructure Management important for CIOs?
CIOs use this capability to maintain a clear view of infrastructure resources and their health. This helps optimise utilisation, plan upgrades, and ensure that infrastructure investments are aligned with service demand
Q: How does IT and Network Infrastructure Management support operations leaders?
It ensures that both legacy and next-generation infrastructure can be monitored and managed consistently, reducing the complexity of hybrid environments. This is essential for operators managing a mix of physical, virtual and cloud-native resources
Q: Why should enterprise architects care about this component?
It provides the foundation for designing scalable, resilient architectures that support new services. Accurate infrastructure management ensures architects can plan effectively for growth and new technology rollouts such as 5G and edge computing
.
Q: What is Location Management used for?
Location Management maintains data about physical and logical locations relevant to services and resources. This includes customer premises, network sites, data centres and logical service areas. It ensures that resources can be accurately associated with the places where they are deployed or consumed
Q: Is Location Management an OSS or BSS function?
Location Management is an OSS function, though it also supports BSS by linking physical addresses to customer accounts and orders. Its primary role is operational, ensuring accurate association between locations, resources and services
Q: Why is Location Management important for operations leaders?
Accurate location data is essential for planning installations, dispatching field engineers and managing resources tied to specific premises or network sites. It improves efficiency and reduces errors in fulfilment and assurance processes
Q: How does Location Management support CIOs and enterprise architects?
For CIOs and architects, this component provides a structured data model for integrating location information across systems. This supports automation and reduces duplication across BSS and OSS functions
Q: Why should CX leaders value Location Management?
It directly impacts fulfilment accuracy. If location data is incorrect, installations fail and customer satisfaction suffers. Ensuring correct address and site management improves first-time-right delivery rates
.
Q: What is Resource Capability Delivery used for?
Resource Capability Delivery manages the allocation and provisioning of network and IT resources required to support services. It translates service requests into specific resource actions, ensuring that the right capabilities are activated to meet customer needs
Q: Is Resource Capability Delivery an OSS or BSS function?
Resource Capability Delivery is an OSS function. It belongs to the operational domain of activating and configuring resources to support services defined at the BSS level
Q: Why is Resource Capability Delivery important for CIOs and enterprise architects?
It provides a structured, automated way to translate business requests into technical resource actions. This reduces manual provisioning, speeds up fulfilment and ensures alignment between commercial offers and network capabilities
Q: How does Resource Capability Delivery support operations leaders?
It allows operations teams to manage provisioning across multiple technologies and vendors. This is critical in multi-vendor, hybrid environments where manual resource management would be too slow and error-prone
Q: Why should CX leaders care about Resource Capability Delivery?
Customers expect fast and accurate service activation. By automating resource capability delivery, operators reduce delays, avoid failed activations and improve satisfaction with new services
.
Q: What is Resource Catalogue Management used for?
Resource Catalogue Management maintains a structured inventory of all technical resources that are available to deliver services. This includes network elements, virtualised functions, IT assets and their capabilities. It acts as the operational counterpart to Product and Service Catalogues, ensuring that the technical capabilities required to fulfil commercial products are accurately defined and accessible
Q: Is Resource Catalogue Management an OSS or BSS function?
Resource Catalogue Management is an OSS function. While Product Catalogue Management (BSS) defines what can be sold, Resource Catalogue Management defines what can be technically delivered. Together they ensure alignment between commercial offers and operational capabilities
Q: Why is Resource Catalogue Management important for CIOs and enterprise architects?
CIOs and architects rely on this component to maintain an accurate mapping between commercial products and the technical resources that support them. This prevents service designs that are commercially attractive but technically unfeasible, and ensures operational scalability
Q: How does Resource Catalogue Management support operations leaders?
Operations leaders use this component to ensure consistent resource definitions across provisioning, activation and monitoring systems. This reduces duplication of effort and improves the efficiency of service delivery processes
Q: Why should product managers care about Resource Catalogue Management?
Although primarily operational, product managers depend on resource catalogue alignment to ensure that their product offers can be delivered reliably. It avoids the risk of overselling services that cannot be technically supported
.
Q: What is Resource Configuration and Activation used for?
Resource Configuration and Activation automates the setup and activation of network and IT resources to deliver services. It takes service orders, translates them into resource-level actions and executes them across different platforms and vendors. This enables rapid provisioning and consistent service activation without manual intervention
Q: Is Resource Configuration and Activation an OSS or BSS function?
This is an OSS function. It is responsible for managing technical resources and ensuring they are configured to deliver services requested at the business level. BSS defines what the customer wants, while this component ensures the operational layer activates it correctly
Q: Why is Resource Configuration and Activation important for CIOs and architects?
CIOs see this component as a cornerstone of automation and orchestration. By standardising resource activation, it reduces provisioning times from days to minutes and supports agile, cloud-native service delivery models
Q: How does Resource Configuration and Activation support operations leaders?
For operations leaders, it reduces reliance on manual provisioning tasks, which are error-prone and time-consuming. Automated activation improves first-time-right fulfilment rates and lowers operational costs
Q: Why should CX leaders value Resource Configuration and Activation?
This component has a direct impact on customer experience, as it determines how quickly and accurately new services are activated. Faster activation means customers can start using services immediately, improving satisfaction and trust
.
Q: What is Resource Discovery and Reconciliation used for?
Resource Discovery and Reconciliation identifies, verifies and synchronises resource data across systems. It detects discrepancies between the actual state of the network or IT environment and the records stored in resource inventories. This ensures accuracy in planning, assurance and fulfilment processes
Q: Is Resource Discovery and Reconciliation an OSS or BSS function?
It is an OSS function. It deals with the technical layer of resources, ensuring that operational data is correct and up to date. While BSS systems rely on accurate information, the responsibility for discovery and reconciliation lies within OSS
Q: Why is Resource Discovery and Reconciliation important for CIOs and architects?
For CIOs, this component is crucial for maintaining data integrity across the architecture. Discrepancies between inventory records and real-world resources cause fulfilment failures, billing errors and compliance risks. Automated reconciliation ensures consistency and reliability
Q: How does Resource Discovery and Reconciliation support operations leaders?
It improves efficiency by eliminating manual audits of network and IT assets. Automated discovery tools provide real-time updates, enabling proactive management of resources and reducing outages caused by incorrect data
Q: Why should CX leaders care about Resource Discovery and Reconciliation?
Although not directly visible to customers, this component ensures that services are delivered and assured correctly. If resource records are inaccurate, orders fail, faults are harder to resolve and customers experience delays or outages
.
Q: What is Resource Inventory used for?
Resource Inventory maintains a complete record of all physical, virtual and logical resources in the organisation’s infrastructure. It tracks their status, attributes, relationships and availability. This provides a single source of truth for operational resource data, supporting planning, fulfilment and assurance activities
Q: Is Resource Inventory an OSS or BSS function?
Resource Inventory is an OSS function. It underpins operational processes by ensuring resources are accurately recorded. BSS functions depend on this data but do not directly manage it
Q: Why is Resource Inventory important for enterprise architects?
It provides the foundation for accurate operational decision-making. We consider Network Inventory to be one of the most pivotal, linchpin functions within the entire OSS/BSS estate. Without a reliable inventory, planning, fulfilment and assurance processes break down, leading to failed orders, billing disputes, poor or incorrect designs and compliance risks. It is pivotal to ensuring consistency across operational domains (network, customer/service/product and systems domains)
Q: How does Resource Inventory support operations leaders?
It enables visibility of resources across the organisation, allowing leaders to optimise utilisation, plan upgrades and manage capacity. By linking inventory with configuration and activation systems, it improves efficiency and reduces errors
Q: Why should CX leaders value Resource Inventory?
Indirectly, this component improves customer experience by ensuring services are delivered accurately and faults are resolved quickly. Inaccurate or outdated inventory data often results in failed activations, delayed fault resolution and dissatisfied customers
.
Q: What is Resource Order Management used for?
Resource Order Management coordinates and executes orders for network and IT resources that are required to fulfil services. When a product or service order is received from the BSS layer, this component decomposes it into resource-level tasks and ensures they are carried out in the correct sequence. It provides tracking, exception handling and visibility of resource fulfilment progress
Q: Is Resource Order Management an OSS or BSS function?
Resource Order Management is an OSS function. While the BSS manages product and service orders from a customer perspective, this component ensures that the underlying resources are correctly provisioned to deliver on those commitments
Q: Why is Resource Order Management important for CIOs and enterprise architects?
CIOs and architects see this component as essential for closing the gap between commercial orders and technical fulfilment. It ensures consistent orchestration of resources across multi-vendor environments, reducing manual intervention and enabling automation
Q: How does Resource Order Management support operations leaders?
Operations leaders rely on this component to manage the complexity of provisioning across diverse technologies and platforms. It reduces failed activations, improves visibility into resource fulfilment and allows for faster service delivery
Q: Why should CX leaders care about Resource Order Management?
Although not customer-facing, this component underpins the reliability of service activation. When resource orders are managed accurately, customers experience fewer delays and failed activations, improving satisfaction and trust
.
Q: What is Resource Test Management used for?
Resource Test Management validates the functionality and performance of network and IT resources. It ensures that resources are working correctly both before they are deployed into service and during ongoing operations. This includes automated testing, fault detection and quality verification of infrastructure components
Q: Is Resource Test Management an OSS or BSS function?
Resource Test Management is an OSS function. It is part of the assurance and operations domain, ensuring that technical resources are reliable. While results may feed into BSS reporting, the testing itself sits firmly within OSS
Q: Why is Resource Test Management important for CIOs and architects?
CIOs value this component as it reduces operational risks by ensuring infrastructure works as expected. Architects see it as essential for validating new technologies before they are scaled up across the network
Q: How does Resource Test Management support operations leaders?
It reduces downtime and operational costs by detecting faults proactively, often before customers are impacted. Automated testing also accelerates the rollout of new technologies by reducing the time needed for manual verification
Q: Why should CX leaders value Resource Test Management?
Customers may not see this function directly, but it ensures service quality and reliability. By catching issues early, operators can avoid outages or degraded service, which directly influences customer satisfaction
.
Q: What is Resource Usage Management used for?
Resource Usage Management collects, processes and analyses usage data generated by network and IT resources. It ensures that all resource consumption is tracked, validated and made available for billing, assurance and analytics. This provides transparency into how resources are being utilised across the organisation
Q: Is Resource Usage Management an OSS or BSS function?
Resource Usage Management is an OSS function. It operates at the technical layer, gathering and processing usage events. While usage data flows into BSS for rating and billing, the collection and validation is handled within OSS
Q: Why is Resource Usage Management important for CFOs and finance leaders?
Accurate usage data ensures that all billable activity is captured and accounted for. For CFOs, this protects revenue, reduces leakage and improves financial accuracy, especially in high-volume transaction environments like mobile data or IoT
Q: How does Resource Usage Management support CIOs and enterprise architects?
It provides a consistent framework for collecting usage across multiple technologies and vendors. This ensures interoperability, reduces integration complexity and supports scalability for new services
Q: Why should CX leaders care about Resource Usage Management?
By enabling real-time usage reporting, this component allows operators to provide customers with transparency about their consumption. This reduces bill shock, builds trust and empowers customers to manage their usage more effectively
.
Q: What is Service Balance Management used for?
Service Balance Management tracks and manages balances for customer services, such as data allowances, prepaid credit, loyalty points or usage thresholds. It ensures that balances are updated in real time and that entitlements are enforced consistently across all services and channels
Q: Is Service Balance Management an OSS or BSS function?
Service Balance Management is primarily an OSS function, although it interacts closely with BSS. It ensures that technical enforcement of balances is consistent across network and service platforms, while BSS consumes balance information for billing and customer communication
Q: Why is Service Balance Management important for CIOs and enterprise architects?
It provides a real-time capability for managing balances across complex product bundles and services. This reduces integration complexity and ensures consistency across systems, especially in converged service environments
Q: How does Service Balance Management support operations leaders?
It ensures operational enforcement of balances, preventing overuse and protecting revenue. By maintaining accurate and timely balance information, operations teams can guarantee compliance with product definitions and service agreements
Q: Why should CX leaders care about Service Balance Management?
Customers expect accurate and real-time balance updates, whether for prepaid services, usage allowances or loyalty programmes. Inaccurate balances lead to disputes and dissatisfaction. By providing transparency and accuracy, this component improves trust and loyalty
.
Q: What is Service Catalog Management used for?
Service Catalog Management provides a centralised definition of all services that can be ordered and delivered. It describes the technical and logical services available, their attributes, rules and dependencies. It acts as the bridge between the Product Catalogue and the Resource Catalogue, ensuring commercial products are accurately mapped to operational capabilities
Q: Is Service Catalog Management an OSS or BSS function?
Service Catalog Management is primarily an OSS function. It defines the operational services that support products, ensuring they can be provisioned, activated and assured. While it interacts with BSS catalogues, its focus is on technical service definitions
Q: Why is Service Catalog Management critical for operators?
It ensures consistency between what is sold commercially and what can be technically delivered. Without this alignment, operators risk overselling services that cannot be provisioned, leading to order fallout, delays and dissatisfied customers
Q: How does Service Catalog Management enable innovation?
By maintaining modular, reusable service definitions, operators can launch new products faster. New services can be built by combining existing components rather than starting from scratch, reducing time-to-market
.
Q: What is Service Inventory used for?
Service Inventory maintains a real-time record of all active services, their status, attributes and relationships to resources and products. It provides a single source of truth for operational service data, supporting fulfilment, assurance and customer support
Q: Is Service Inventory an OSS or BSS function?
Service Inventory is an OSS function. It provides the operational view of services, ensuring accuracy in delivery and assurance processes. While BSS systems may reference service information, the operational control belongs to OSS
Q: Why is Service Inventory important for operators?
Accurate service inventory ensures services can be delivered, monitored and assured consistently. If service data is incomplete or incorrect, orders fail, faults cannot be resolved efficiently and billing errors occur. It is a foundational component for operational accuracy
Q: How does Service Inventory support customer operations?
It provides visibility into the services a customer is using, their current status and any dependencies. This improves the ability to resolve issues quickly and reduces repeat interactions caused by inconsistent records
.
Q: What is Service Order Management used for?
Service Order Management handles the orchestration and execution of service-level orders derived from product orders. It decomposes orders into the necessary service activities, coordinates fulfilment across systems and ensures delivery is tracked through to completion
Q: Is Service Order Management an OSS or BSS function?
Service Order Management is an OSS function. It operates at the service level, translating commercial product orders (BSS) into technical fulfilment steps required for activation
Q: Why is Service Order Management essential?
It provides the link between commercial ordering and operational delivery. Without structured service order management, fulfilment becomes fragmented and error-prone, increasing order fallout and delaying service activation
Q: How does Service Order Management improve efficiency?
It automates the breakdown of orders and coordinates execution across multiple domains. This reduces manual work, improves first-time-right activations and accelerates service delivery
.
Q: What is Service Qualification Management used for?
Service Qualification Management determines whether a service can be delivered to a customer at a specific location. It checks availability, feasibility and capability, ensuring that orders are only accepted when they can be successfully fulfilled
Q: Is Service Qualification Management an OSS or BSS function?
It is an OSS function, although it is often invoked by BSS processes during sales and ordering. It ensures that technical feasibility checks are applied before commitments are made to the customer
Q: Why is Service Qualification Management important for operators?
It prevents service orders from being accepted when they cannot be delivered. This reduces order fallout, avoids customer disappointment and improves operational efficiency by ensuring only feasible requests enter fulfilment processes
Q: How does Service Qualification Management support customer experience?
By providing accurate qualification results at the point of sale, customers receive realistic expectations about what services are available. This improves trust and reduces failed activations or cancelled orders
.
Q: What is Service Quality Management used for?
Service Quality Management monitors, measures and manages the performance of services to ensure they meet defined service level agreements (SLAs) and quality targets. It provides analytics, alarms and reporting that allow operators to identify service degradation, track compliance and take corrective action
Q: Is Service Quality Management an OSS or BSS function?
Service Quality Management is an OSS function. It is focused on the operational performance of services, ensuring that technical delivery matches business and customer expectations. Results may feed into BSS systems for SLA reporting, but the function itself is operational
Q: Why is Service Quality Management critical for operators?
It ensures that services are delivered as promised, protecting revenue and customer satisfaction. Without this component, operators risk undetected degradation, leading to churn and SLA penalties. It also provides the data needed to demonstrate compliance to enterprise customers
Q: How does Service Quality Management improve efficiency?
By providing proactive monitoring and analysis, it allows issues to be addressed before they become major incidents. This reduces downtime, improves operational responsiveness and lowers costs associated with reactive fault handling
.
Q: What is Service Test Management used for?
Service Test Management validates that services function correctly both during provisioning and on an ongoing basis. It runs test scenarios, monitors outcomes and ensures that services meet expected performance before they are handed over to customers
Q: Is Service Test Management an OSS or BSS function?
It is an OSS function. While it interacts with BSS by feeding back results that affect customer commitments, the execution of service testing is an operational task that belongs in the OSS domain
Q: Why is Service Test Management important for operators?
It reduces the risk of failed activations or service degradation going unnoticed. By testing services proactively, operators can ensure that customer experiences align with expectations, avoiding disputes and complaints after launch
Q: How does Service Test Management support service delivery?
It enables first-time-right activations by validating services before they go live. It also provides ongoing monitoring that helps operators maintain high service quality over time
.
Q: What is Service Usage Management used for?
Service Usage Management collects, validates and processes service usage data, ensuring it is accurate and consistent for billing, analytics and assurance. It provides the business view of usage, linking events to services and customers in a way that supports financial and operational processes
Q: Is Service Usage Management an OSS or BSS function?
It is an OSS function with strong ties to BSS. While OSS is responsible for collecting and validating usage, BSS consumes this data to calculate charges and provide customer-facing reports
Q: Why is Service Usage Management essential?
It ensures that every service consumption event is tracked and accounted for, protecting revenue and preventing leakage. It also supports transparency, enabling customers to access accurate usage information in real time
Q: How does Service Usage Management support operational reliability?
By providing consistent usage records, it reduces discrepancies across systems and ensures that both assurance and billing processes are working with accurate data. This minimises disputes and improves confidence in reporting
.
Q: What is Strategic Resource Planning used for?
Strategic Resource Planning provides long-term forecasting and planning for network and IT resources. It analyses capacity, utilisation and demand trends to inform investment decisions and ensure resources are available to support future services
Q: Is Strategic Resource Planning an OSS or BSS function?
Strategic Resource Planning is an OSS function. It focuses on the operational domain of infrastructure planning and optimisation. Its outputs, however, are often used by BSS functions to support commercial decision-making
Q: Why is Strategic Resource Planning critical for operators?
It ensures that investments in infrastructure are aligned with demand, avoiding both under-provisioning, which leads to service failures, and over-provisioning, which wastes capital. It also supports the introduction of new technologies such as 5G and edge computing by forecasting their impact on resources
Q: How does Strategic Resource Planning improve efficiency?
It enables data-driven decision-making for infrastructure investment, reducing costs and improving return on capital. By forecasting demand accurately, it helps operators deploy resources proactively rather than reactively
.
Q: What is Trouble Ticket Management used for?
Trouble Ticket Management handles the creation, tracking and resolution of trouble tickets when incidents or service issues occur. It provides a structured way to manage faults and customer complaints, assigning responsibilities, prioritising issues and ensuring timely resolution
Q: Is Trouble Ticket Management an OSS or BSS function?
Trouble Ticket Management is primarily an OSS function, though it overlaps with BSS. It operates in the operational domain to resolve technical issues, but tickets are often linked to customer records in BSS to provide end-to-end visibility across support and assurance
Q: Why is Trouble Ticket Management critical for operators?
It provides the backbone for incident resolution. Without structured ticketing, issues can be lost, duplicated or delayed. Trouble Ticket Management ensures accountability, improves resolution times and supports compliance with SLAs
Q: How does Trouble Ticket Management improve customer outcomes?
By tracking issues from detection to resolution, operators can communicate clearly with customers, set realistic expectations and demonstrate progress. This transparency improves customer trust, even when service disruptions occur
.
Q: What is Workforce Administration used for?
Workforce Administration manages the people and skills available to deliver operational tasks, such as installations, repairs and maintenance. It provides capabilities for resource allocation, scheduling, skills management and performance monitoring
Q: Is Workforce Administration an OSS or BSS function?
It is an OSS function. While HR systems manage employment and payroll, Workforce Administration focuses on the operational deployment of staff and contractors for service delivery and assurance
Q: Why is Workforce Administration important for operators?
It ensures the right person with the right skills is available at the right time to complete tasks. This improves operational efficiency, reduces downtime and supports faster service delivery
Q: How does Workforce Administration impact customer experience?
By ensuring field engineers and support staff are deployed efficiently, customers benefit from quicker installations and faster resolution of issues. Poor workforce management often translates directly into customer dissatisfaction
.
Q: What is Workforce Management used for?
Workforce Management optimises the scheduling, dispatch and tracking of workforce activities. It ensures that tasks are assigned based on availability, location and skills, while also providing real-time visibility of progress and status updates
Q: Is Workforce Management an OSS or BSS function?
Workforce Management is an OSS function. It sits within the operational domain, managing the execution of workforce tasks required for fulfilment and assurance activities
Q: Why is Workforce Management critical for operators?
It increases efficiency by reducing travel time, improving scheduling accuracy and maximising resource utilisation. This lowers operational costs while maintaining service quality
Q: How does Workforce Management improve transparency?
It provides real-time updates on job progress, allowing both operators and customers to track task status. This transparency reduces uncertainty, improves communication and enhances customer trust
.
Q: What is Accounting Management used for?
Accounting Management ensures accurate financial tracking of resource, service and product usage. It collects accounting data, applies business rules and prepares records for downstream billing and financial systems. It provides transparency and consistency between operational activities and financial reporting
Q: Is Accounting Management an OSS or BSS function?
Accounting Management is a hybrid but leans towards OSS. It captures operational usage and event data, but its outputs are consumed by BSS for billing and revenue management. Its role is to provide accurate financial event data at the operational layer
Q: Why is Accounting Management critical for operators?
It prevents revenue leakage by ensuring all chargeable events are properly accounted for. It also enables auditability and compliance, ensuring that reported revenues match actual service usage
Q: How does Accounting Management improve efficiency?
By standardising accounting records across systems, it reduces discrepancies between OSS and BSS. This lowers dispute rates, improves billing accuracy and supports regulatory compliance
.
Q: What is Anomaly Management used for?
Anomaly Management detects and analyses unusual patterns in data that may indicate faults, fraud, misconfigurations or emerging service issues. It uses analytics and AI to spot deviations from expected behaviours in networks, services or usage patterns
Q: Is Anomaly Management an OSS or BSS function?
Anomaly Management is primarily an OSS function, although its insights can be used by BSS for fraud prevention, billing assurance and customer experience improvements
Q: Why is Anomaly Management important?
It provides early warning of potential issues, allowing operators to intervene before they escalate. This reduces downtime, prevents revenue loss and helps maintain compliance with service level agreements
Q: How does Anomaly Management support customer satisfaction?
By identifying problems before customers notice them, operators can proactively address service degradations and communicate transparently. This improves trust and reduces complaint volumes
.
Q: What is Campaign Management used for?
Campaign Management designs, executes and tracks marketing campaigns targeted at specific customer segments. It manages campaign rules, channel execution and performance analysis to ensure campaigns are effective and measurable
Q: Is Campaign Management an OSS or BSS function?
Campaign Management is a BSS function. It operates within the commercial layer, focusing on customer engagement and marketing effectiveness rather than technical operations
Q: Why is Campaign Management important for operators?
It enables operators to deliver personalised, data-driven campaigns that improve customer acquisition, cross-sell and upsell opportunities. Effective campaign management increases revenue and reduces churn by ensuring offers are relevant
Q: How does Campaign Management improve efficiency?
It automates campaign execution across multiple channels and provides performance insights. This reduces manual effort, improves targeting accuracy and enables continuous optimisation
.
Q: What is Experience Insight Management used for?
Experience Insight Management collects and analyses customer experience data across touchpoints, products and services. It provides insights into customer perceptions, satisfaction and pain points, helping operators improve overall experience
Q: Is Experience Insight Management an OSS or BSS function?
It is primarily a BSS function, though it consumes OSS data such as service performance and fault records. Its focus is on analysing and improving the customer’s end-to-end journey
Q: Why is Experience Insight Management critical?
Customer experience is a key differentiator in competitive markets. This component enables operators to identify weak points in the journey and take targeted actions to improve satisfaction and reduce churn
Q: How does Experience Insight Management support decision-making?
By combining operational and behavioural data, it provides a holistic view of customer sentiment. This enables product, marketing and service teams to make data-driven improvements that align with customer expectations
.
Q: What is Knowledge Management used for?
Knowledge Management captures, organises and makes available structured and unstructured knowledge for use across the organisation. This includes technical documentation, troubleshooting guides, best practices, FAQs and lessons learned. It ensures that staff and customers can access consistent and accurate information when needed
Q: Is Knowledge Management an OSS or BSS function?
Knowledge Management is a cross-cutting BSS function, as it primarily supports customer care, sales and service teams. However, it also integrates with OSS by making technical troubleshooting knowledge available for operations teams
Q: Why is Knowledge Management important?
It reduces resolution times, improves first-time-right fixes and ensures consistency across support channels. Without this component, staff often duplicate effort or rely on outdated information, leading to inefficiency and errors
Q: How does Knowledge Management improve customer outcomes?
By empowering customer service representatives and self-service channels with accurate knowledge, customers receive faster, more accurate responses to their issues. This directly improves satisfaction and lowers call volumes
.
Q: What is Recommendation Management used for?
Recommendation Management uses analytics and AI to provide personalised product, service and action recommendations to customers and staff. This includes upsell and cross-sell suggestions, troubleshooting steps, and next-best-action guidance in customer journeys
Q: Is Recommendation Management an OSS or BSS function?
It is a BSS function, as it directly influences customer engagement, sales and service interactions. However, it may consume OSS data such as service performance to inform context-aware recommendations
Q: Why is Recommendation Management valuable?
It increases revenue by delivering tailored offers at the right time, and it reduces churn by proactively suggesting solutions to customer issues. Personalisation is a key differentiator in digital service markets
Q: How does Recommendation Management improve efficiency?
By automating the decisioning process, it reduces manual effort for staff and ensures consistent, data-driven interactions. This makes campaigns and support processes more effective and scalable
.
Q: What is Product/Sales Performance Management used for?
Product/Sales Performance Management tracks and analyses the performance of products and sales activities. It provides insights into revenue, profitability, adoption rates and channel effectiveness, helping operators optimise their portfolio and sales strategies
Q: Is Product/Sales Performance Management an OSS or BSS function?
It is a BSS function. Its role is commercial, focusing on sales and product success in the market rather than technical delivery
Q: Why is Product/Sales Performance Management important?
It ensures operators understand which products and sales channels are driving growth and which are underperforming. This allows for targeted improvements, rationalisation and investment decisions based on real performance data
Q: How does Product/Sales Performance Management support growth?
By identifying successful products and strategies, it enables operators to replicate winning approaches and scale them. At the same time, it provides evidence for discontinuing or adjusting weak offerings
.
Q: What is Resource Performance Management used for?
Resource Performance Management monitors and analyses the performance of network and IT resources. It tracks metrics such as utilisation, availability, latency and throughput to ensure that resources operate within expected parameters
Q: Is Resource Performance Management an OSS or BSS function?
It is an OSS function. Its focus is technical, ensuring that the infrastructure supporting services is optimised and reliable
Q: Why is Resource Performance Management essential?
It ensures that infrastructure investments deliver the expected performance and availability. Without this, operators risk resource bottlenecks, degraded services and wasted capacity
Q: How does Resource Performance Management support operations?
By providing insights into trends and anomalies, it allows proactive tuning and capacity management. This prevents issues before they impact services and customers
.
Q: What is Service Performance Management used for?
Service Performance Management tracks and analyses the quality and performance of services delivered to customers. It measures KPIs such as uptime, latency, throughput and SLA compliance, providing a holistic view of service health
Q: Is Service Performance Management an OSS or BSS function?
It is an OSS function. While its results feed into BSS systems for SLA reporting and customer communications, the measurement and monitoring itself is operational in nature
Q: Why is Service Performance Management important?
It provides the visibility needed to ensure services meet contractual and customer expectations. Without it, operators cannot assure quality, leading to churn and potential SLA penalties
Q: How does Service Performance Management improve business outcomes?
By linking service quality to customer experience and contracts, it helps operators prioritise investments, prevent churn and strengthen relationships with enterprise customers who demand strict SLAs
.
The ODA Component Library is comprehensive in covering the building blocks of OSS and BSS, but when we compare it to the categories of software that are commonly deployed by operators, there are some notable gaps and differences in emphasis to what’s currently provided by the market.
Here are some examples (but not exhaustive):
Q: What is CPQ used for?
CPQ automates the process of configuring complex telecom products and services, applying pricing rules, managing discounts and generating accurate quotes for customers. It ensures sales proposals are valid, fulfilment-ready and commercially sound, reducing errors and speeding up the sales cycle
Q: Is CPQ an OSS or BSS function?
CPQ is a BSS function. It operates in the commercial layer, linking directly to product catalogue and order management but focused on customer-facing sales activities
Q: Why is CPQ important for operators?
It shortens sales cycles, reduces manual errors and ensures that what is sold can actually be delivered. This is particularly important in B2B and enterprise contracts where deals often involve multi-site and multi-service bundles
Q: What are the gaps between ODA and typical CPQ offerings?
ODA spreads CPQ functionality across several components such as Product Configurator, Product Order Capture and Product Catalogue Management, but it does not define CPQ as a single integrated capability. In practice, operators usually deploy CPQ as a dedicated system that unifies all these functions end-to-end
.
Q: What is CRM used for?
CRM consolidates customer data, interactions and history across sales, marketing and service functions. It provides a single view of the customer, ensuring consistent, personalised and efficient engagement across all channels
Q: Is CRM an OSS or BSS function?
CRM is a BSS function. It sits in the commercial and customer-facing layer, supporting sales, care and marketing processes
Q: Why is CRM important for operators?
It enables operators to manage millions of customer relationships consistently, track their needs and history, and ensure smooth handovers across sales and service channels. Without CRM, interactions become fragmented, leading to poor customer experience and churn
Q: What are the gaps between ODA and typical CRM offerings?
ODA decomposes CRM into multiple fine-grained components such as Party Management, Lead & Opportunity Management and Party Interaction Management. This modular approach makes sense in ODA, but it does not align directly with how most operators buy CRM as a single integrated platform
.
Q: What is GIS used for in telecoms?
GIS provides spatial mapping and geolocation capabilities for network assets, customer locations and service coverage. It supports network planning, service qualification, assurance and field service optimisation
Q: Is GIS an OSS or BSS function?
GIS acts as a broad support function. It underpins planning, fulfilment and assurance activities, which are OSS in nature, but also supports BSS use cases like service qualification during sales
Q: Why is GIS critical for operators?
Accurate location intelligence is essential for planning network builds, qualifying service availability and efficiently dispatching field engineers. Without GIS, operators risk overbuilding, underutilising resources or providing incorrect information to customers
Q: What are the gaps between ODA and typical GIS offerings?
ODA includes Location Management and Resource Inventory, which depend on geospatial data, but there is no dedicated GIS component. This underrepresents the importance of GIS as a standalone category in most OSS stacks
.
Q: What is AIOps used for?
AIOps applies artificial intelligence and machine learning to IT and network operations. It analyses large volumes of operational data to detect anomalies, predict issues, correlate alarms and automate resolution, enabling self-healing networks
Q: Is AIOps an OSS or BSS function?
AIOps is primarily an OSS function but can incorporate other data streams such as customer sentiment to guide its NBA (Next Best Action) advisory. It enhances assurance and operations by automating monitoring and resolution, though its insights may also support BSS in areas such as fraud prevention or customer communications
Q: Why is AIOps important for operators?
Modern networks generate too much data for manual monitoring. AIOps reduces operational noise, speeds up root cause analysis, lowers costs and improves reliability by preventing outages before they impact customers
Q: What are the gaps between ODA and typical AIOps offerings?
ODA includes components like Anomaly Management, Fault Management and Resource Performance Management that could leverage AI, but it does not explicitly define AIOps as a capability. This underplays the shift operators are making towards AI-driven autonomous operations
.
Q: What is FSM used for?
FSM coordinates the scheduling, routing and task management of field engineers and contractors. It integrates workforce availability, skills and inventory with geospatial data to optimise service delivery and reduce costs
Q: Is FSM an OSS or BSS function?
FSM is an OSS function, supporting assurance and fulfilment tasks. It also connects to BSS when customers need appointment booking and notifications
Q: Why is FSM critical for operators?
Field operations are often the most customer-visible part of the operator’s service. Efficient FSM ensures faster installations, reduced missed appointments and improved customer satisfaction, while also lowering operational costs
Q: What are the gaps between ODA and typical FSM offerings?
ODA includes Workforce Management and Work Order Management, but it does not explicitly integrate GIS and inventory data into a unified FSM capability. In practice, telcos deploy FSM as a dedicated solution that tightly couples these domains
.
Q: What is Revenue Assurance used for?
Revenue Assurance ensures that all services consumed are correctly billed, rated and collected, preventing revenue leakage. It validates data integrity across mediation, rating, billing and collections processes
Q: What is Fraud Management used for?
Fraud Management detects and prevents fraudulent activities such as SIM fraud, roaming abuse and bypass fraud. It analyses usage patterns in near real-time to prevent losses and protect customers
Q: Are Revenue Assurance and Fraud Management OSS or BSS functions?
Both are BSS functions, as they are tied to financial management and billing processes. They rely heavily on OSS usage data but operate at the commercial and financial layer
Q: What are the gaps between ODA and typical Revenue Assurance and Fraud Management offerings?
ODA touches on these areas with Accounting Management, Anomaly Management and Debt Collection Management, but it does not define them as standalone capabilities. In reality, operators treat Revenue Assurance and Fraud Management as distinct system categories in their BSS stacks
.
Q: What is Partner and Ecosystem Management used for?
It manages partner relationships, onboarding, settlements and revenue sharing across ecosystems. It enables operators to launch marketplaces, co-deliver services and manage partner lifecycles efficiently
Q: Is Partner and Ecosystem Management an OSS or BSS function?
It is a BSS function. It focuses on commercial engagement and financial settlement with partners rather than operational network management
Q: Why is Partner and Ecosystem Management important?
Telecoms are shifting towards platform business models, where ecosystem partners provide digital services, IoT solutions or 5G slices. Without structured partner management, onboarding and settlements become slow and prone to disputes
Q: What are the gaps between ODA and typical Partner and Ecosystem Management offerings?
ODA covers Agreement Management and Party Roles & Permissions, but it does not define Partner Lifecycle Management or Marketplace Orchestration as standalone components. These are increasingly critical as operators move towards multi-party digital ecosystems
.
Q: What are Project Management tools used for in telecoms?
Project Management tools support the implementation planning, execution and tracking of transformation projects, network rollouts and system upgrades. They manage timelines, resources, dependencies and risks across complex, multi-stakeholder programmes. We use WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) tools extensively to plan and track the complexities of large OSS/BSS transformation projects.
Q: Is Project Management an OSS or BSS function?
Project Management is neither an OSS nor BSS function in the strict sense. It sits more in the enterprise IT and portfolio management layer, supporting delivery of OSS/BSS and network initiatives rather than running in production systems
Q: Why are Project Management tools important for operators?
Large-scale telecom initiatives such as network rollouts or BSS transformations involve hundreds of interdependent tasks. Project Management tools provide structure, accountability and reporting to keep these programmes on track
Q: What are the gaps between ODA and typical Project Management offerings?
ODA does not define a Project Management component, as it focuses on operational and business support systems rather than delivery management. However, in practice, operators rely heavily on Project Portfolio Management (PPM) platforms (e.g. Jira, MS Project, Clarity PPM) alongside ODA-aligned systems
.
Q: What are ITSM tools used for in telecoms?
ITSM tools manage IT operations processes such as incident, problem, change and service request management. They provide workflows, ticketing, approvals and audit trails that underpin IT governance and operational discipline
Q: Is ITSM an OSS or BSS function?
ITSM sits alongside OSS. It is not directly involved in service fulfilment or assurance, but it manages the IT operations processes that support both OSS and BSS. Many operators integrate OSS/BSS alarms and tickets into ITSM platforms for end-to-end incident handling
Q: Why are ITSM tools important for operators?
They provide structure and governance for IT and network operations, ensuring compliance with ITIL and regulatory frameworks. Without ITSM, incident response and change management become chaotic and risky
Q: What are the gaps between ODA and typical ITSM offerings?
ODA includes components like Fault Management, Problem Management and Work Order Management, which overlap with ITSM concepts. However, ODA does not provide a dedicated ITSM layer. In practice, operators often use ServiceNow, BMC Remedy or Jira Service Management to integrate ITSM with OSS and BSS
.
At PAOSS we specialise in helping operators and enterprises navigate the complexity of OSS and BSS. Whether you are trying to understand how ODA components align with real-world product categories, shortlist vendors or plan your future roadmap, we provide tailored guidance.
Our OSS/BSS Vendor Directory connects you with hundreds of the most relevant solutions on the market, while our advisory services (such as Vendor Selection Processes) help you identify best-fit technologies and avoid costly missteps.
We also work with clients to design practical roadmaps that balance short-term needs with long-term transformation goals.
If you are looking for clarity on which solutions best match your requirements, or how to align your OSS/BSS strategy with ODA, we can help. Fill in the form below and one of our experts will get in touch to discuss your priorities and next steps